

| Distributed
Coding of
Correlated Sources and Applications in Sensor Networks |
| Joint Compression-Routing for Networks |
|
Introduction
:
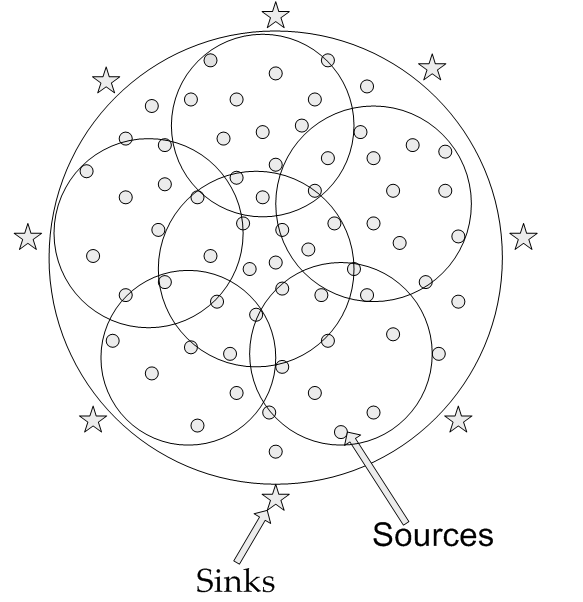 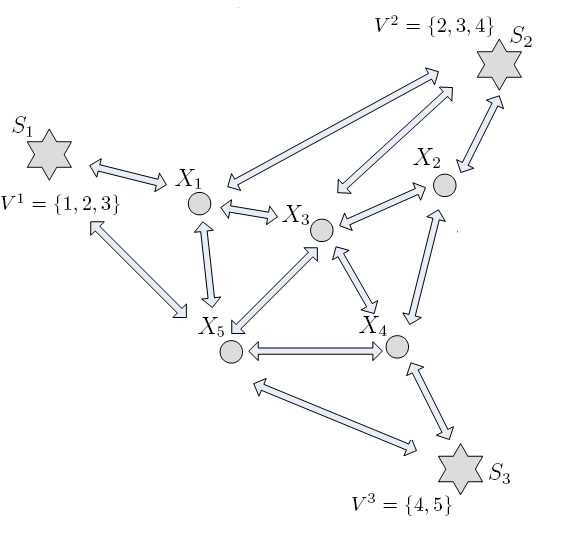 An integral part of optimizing resources in communication networks is routing of information. In this work we consider the problem of minimizing the communication cost for a general multi-hop network with correlated sources and multiple sinks. A typical multi-hop network is shown in the figure. This problem is a very recent and exciting development within this project and forms the preliminary basis for a new project funded by NSF under grant CCF-1016861. As part of the new project, we will be fully pursuing this and related directions. Let a network G be given with N source nodes, M sinks and |V | − N −M intermediate nodes. Each edge e is a network link whose communication cost depends on the edge weight we. Source node i observes random variable Xi. Each sink Sj requests for a subset of sources represented by Vj . Conversely each source Vi is to be reconstructed at a subset of sinks denoted by Si. Our objective is to design joint coding-routing schemes to minimize the overall network cost (calculated given the set of link rates and edge weights) for reconstruction of source information at appropriate sinks. For the single sink scenario, it has been shown that this problem can be decoupled, without loss of optimality, into two separate subproblems of distributed source coding and finding the optimal routing (transmission structure). It has further been established that, under certain assumptions, such decoupling also applies in the general case of multiple sinks and arbitrary network demands. We showed that these assumptions are significantly restrictive, and further provided examples to substantiate the loss, including settings where removing the assumptions yields unbounded performance gains. An approach to solving the unconstrained problem, where routing and coding cannot be decoupled, was derived based on Han and Kobayashi’s achievability region for multi-terminal coding. Related publications: K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K.Rose, "Towards Optimum Cost in Multi-hop Networks with Arbitrary Network Demands ", Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), June 2010. 
|
|
Dispersive
Information Routing:
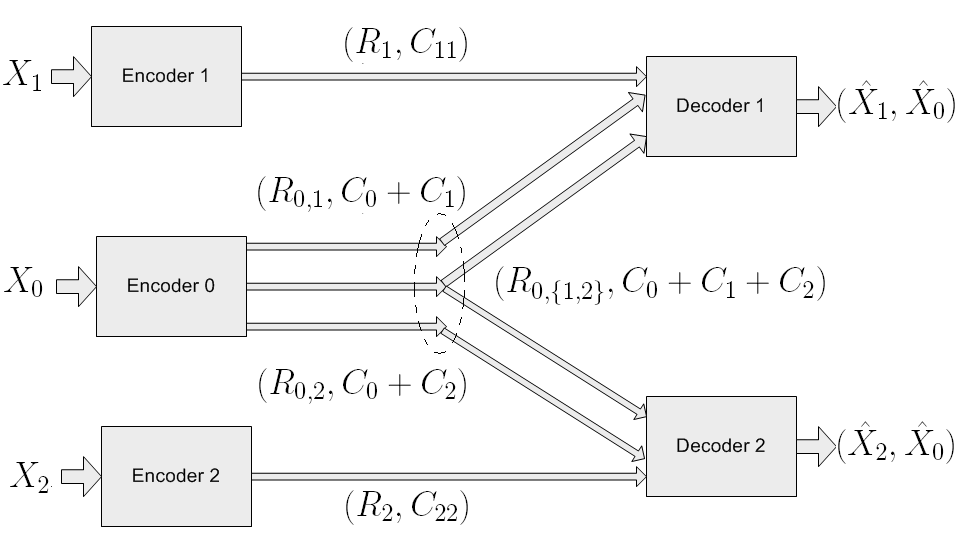 We
introduced a new routing paradigm, called dispersive information
routing, wherein the intermediate nodes are allowed to forward a subset
of the received bits on subsequent paths. This paradigm opens up a rich
class of research problems which focus on the interplay between
encoding and routing in a network. What makes it particularly
interesting is the challenge in encoding sources such that, exactly the
required information is routed to each sink, to reconstruct the sources
they are interested in. We demonstrated using simple examples that our
approach offers better asymptotic performance than conventional routing
techniques. We also introduced a variant of the well known random
binning technique, called ‘power binning’, to encode and decode sources
that are dispersively transmitted, and which asymptotically achieves
the minimum communication cost within this routing paradigm. We
introduced a new routing paradigm, called dispersive information
routing, wherein the intermediate nodes are allowed to forward a subset
of the received bits on subsequent paths. This paradigm opens up a rich
class of research problems which focus on the interplay between
encoding and routing in a network. What makes it particularly
interesting is the challenge in encoding sources such that, exactly the
required information is routed to each sink, to reconstruct the sources
they are interested in. We demonstrated using simple examples that our
approach offers better asymptotic performance than conventional routing
techniques. We also introduced a variant of the well known random
binning technique, called ‘power binning’, to encode and decode sources
that are dispersively transmitted, and which asymptotically achieves
the minimum communication cost within this routing paradigm. Related publication: K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K. Rose, "Lossy Common Information of Two Dependent Random Variables", To appear in Proc. IEEE Symp. Information Theory (ISIT), July, 2012. K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K. Rose, "An Optimal Transmit-Receive Rate Tradeoff in Gray-Wyner Network and Its Relation to Common Information", Proc. IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), October 2011.  K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K. Rose, "An Achievable Rate Region for Distributed Source Coding and Dispersive Information Routing", Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), July 2011.  (Pre-print) (Pre-print)K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, K. Rose, “On optimum communication cost for joint compression and dispersive information routing,” Proc. IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), August 2010.  |
|
Dispersive Information Router
Design:
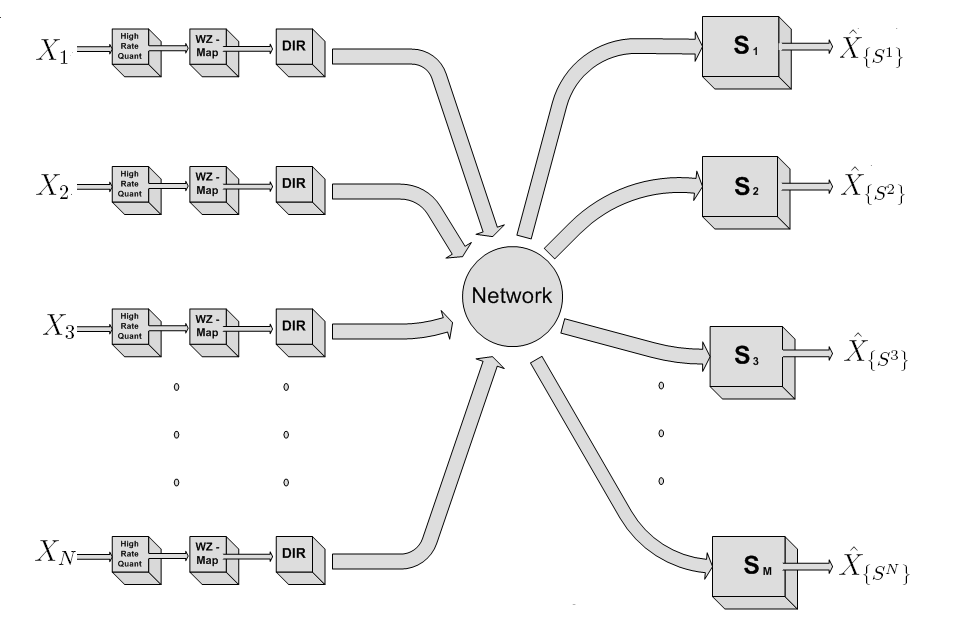 Inspired
by our recent work on distributed source coding and fusion coding, we
proposed a practical design approach to implement dispersive
information routing. We demonstrated the close similarities between
dispersive information routing, fusion coding
and large scale
distributed coding. Central to all the problems is a module
which
selectively extracts only the "useful information" for decoding. In the
DIR setup, the network selectively forwards a subset of the transmitted
bits to the relevant sinks to optimize the cost. In the fusion coding
setting, the database tries to retrieve only the useful information for
decoding each query. In the large scale distributed coding setup, the
decoder selects a subset of the received bits to reduce decoder storage
complexity. Inspired
by our recent work on distributed source coding and fusion coding, we
proposed a practical design approach to implement dispersive
information routing. We demonstrated the close similarities between
dispersive information routing, fusion coding
and large scale
distributed coding. Central to all the problems is a module
which
selectively extracts only the "useful information" for decoding. In the
DIR setup, the network selectively forwards a subset of the transmitted
bits to the relevant sinks to optimize the cost. In the fusion coding
setting, the database tries to retrieve only the useful information for
decoding each query. In the large scale distributed coding setup, the
decoder selects a subset of the received bits to reduce decoder storage
complexity. We showed using synthetically generated Gaussian sensor grids that, dispersive information routing gains about 1 dB in distortion over conventional routing. Equivalently, we gain about 1 dB in cost for a fixed distortion. Related publication: K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, S. Ramaswamy and K.Rose, "Distributed source coding and dispersive information routing: an integrated approach with networking and database applications,” European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), (invited), special session on Distributed Source Coding, August 2010.  |
|
Multiple Descriptions Coding: 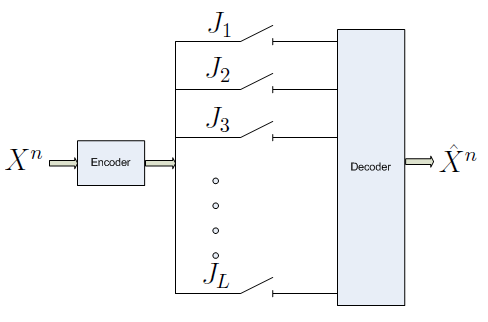 Multiple
descriptions (MD) problem was introduced in late seventies in the
information theory community with a motivation towards packet switched
networks. The setup involves L channels between a source and a sink,
out of which a subset of the channels are assumed to fail. The encoder
generates L descriptions, each sent on one of the channels. Depending
on the failure, a subset of these L descriptions are lost. It is
assumed that the the encoder is unaware of which channels might fail.
The objective is to design the L descriptions and the decoders (for
each possible received combination of descriptions) with respect to an
over all rate-distortion trade-off. The general problem has remained
challenging and unsolved. We proposed a new encoding technique called
`combinatorial message sharing' using principles from dispersive
information routing and showed that the new achievable region is strictly larger than the most popular region for this setup so far due to Venkataramani, Kramer and Goyal. Multiple
descriptions (MD) problem was introduced in late seventies in the
information theory community with a motivation towards packet switched
networks. The setup involves L channels between a source and a sink,
out of which a subset of the channels are assumed to fail. The encoder
generates L descriptions, each sent on one of the channels. Depending
on the failure, a subset of these L descriptions are lost. It is
assumed that the the encoder is unaware of which channels might fail.
The objective is to design the L descriptions and the decoders (for
each possible received combination of descriptions) with respect to an
over all rate-distortion trade-off. The general problem has remained
challenging and unsolved. We proposed a new encoding technique called
`combinatorial message sharing' using principles from dispersive
information routing and showed that the new achievable region is strictly larger than the most popular region for this setup so far due to Venkataramani, Kramer and Goyal. Related publication: E. Akyol, K. Viswanatha and K. Rose, "Combinatorial Message Sharing and Random Binning for Multiple Descriptions Coding," To appear in IEEE Int. Symp. Information Theory (ISIT), July 2012. K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K. Rose, "A Strictly Improved Achievable Region for Multiple Descriptions Using Combinatorial Message Sharing", Proc. IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), October 2011.  K. Viswanatha, E. Akyol, and K. Rose, "Combinatorial Message Sharing for a Refined Multiple Descriptions Achievable Region", Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), July 2011.  (Pre-print) (Pre-print) |
SCL's Source coding and quantization archive

