Fusion storage and selective retrieval of correlated sources
Research Directions:
Information theoretic analysis of lossless fusion coding
Fusion coder design for storage and selective retrieval
Shared description fusion coding
Predictive fusion coding

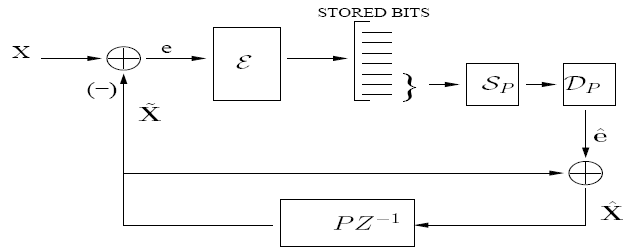
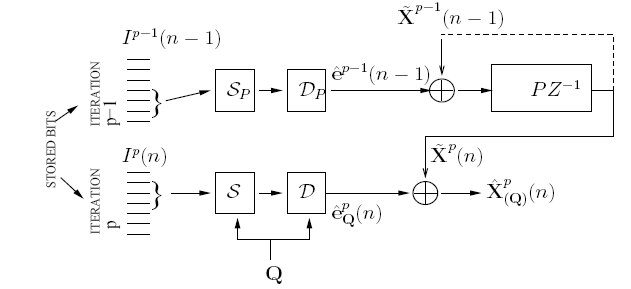
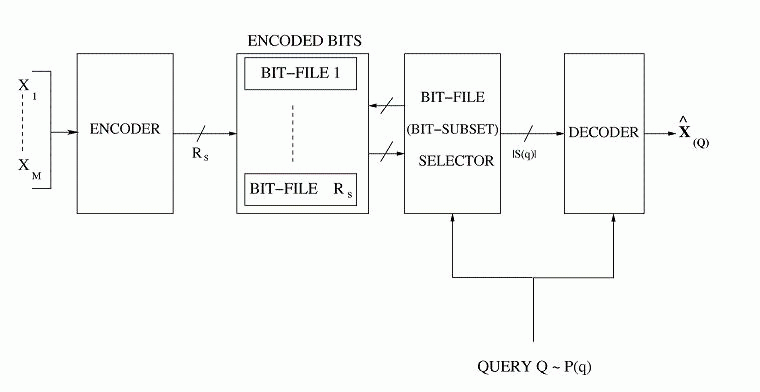 Based on our earlier work on optimized storage and fast selective retrieval of correlated streams of data, we developed information theoretical models that estimate gains possible with selective information retrieval over naive storage techniques. We then formulated a Lagrangian cost function that is a weighted sum of the source and query averaged distortion and the query-averaged retrieval rate, at a given storage complexity. The optimization of this cost over a training set of sample inputs and sample queries reduces to the design of an encoding rule, a mapping from queries to subset of encoded bits and code-books for different subsets of bits. We derived the necessary conditions for optimality and minimized the cost function by iteratively enforcing the necessary conditions for optimality. Since each condition for optimality results in a reduced Lagrangian cost, the algorithm is guaranteed to converge in a few iterations. We investigated the performance of the algorithm over synthetic and real data sets for query distributions representing expected user behavior and compared the results with naive storage techniques - namely joint compression, and separate compression.
Based on our earlier work on optimized storage and fast selective retrieval of correlated streams of data, we developed information theoretical models that estimate gains possible with selective information retrieval over naive storage techniques. We then formulated a Lagrangian cost function that is a weighted sum of the source and query averaged distortion and the query-averaged retrieval rate, at a given storage complexity. The optimization of this cost over a training set of sample inputs and sample queries reduces to the design of an encoding rule, a mapping from queries to subset of encoded bits and code-books for different subsets of bits. We derived the necessary conditions for optimality and minimized the cost function by iteratively enforcing the necessary conditions for optimality. Since each condition for optimality results in a reduced Lagrangian cost, the algorithm is guaranteed to converge in a few iterations. We investigated the performance of the algorithm over synthetic and real data sets for query distributions representing expected user behavior and compared the results with naive storage techniques - namely joint compression, and separate compression.