Introduction
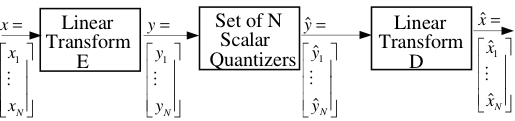 Transform coding is an alternative to predictive coding to compress sources with memory. While the optimal transform for Gaussian sources is known to be Karhunen Loeve Transform (KLT), the transform coding problem of non-Gaussian sources remain largely an open problem, due to the dependence of quantization error to the source distribution. This dependency is highlighted in the distributed transform coding case where quantizations typically involve Wyner-Ziv mappings. As a remedy, we investigated the optimal transform in conjunction with dithered quantization since dithered quantization provides reconstruction errors that are independent of the source distribution. We derived the optimal transform which is KLT followed by a diagonal scaling matrix that depends on the bit allocation. This transform is optimal for all sources with fixed rate dithered quantization.
Transform coding is an alternative to predictive coding to compress sources with memory. While the optimal transform for Gaussian sources is known to be Karhunen Loeve Transform (KLT), the transform coding problem of non-Gaussian sources remain largely an open problem, due to the dependence of quantization error to the source distribution. This dependency is highlighted in the distributed transform coding case where quantizations typically involve Wyner-Ziv mappings. As a remedy, we investigated the optimal transform in conjunction with dithered quantization since dithered quantization provides reconstruction errors that are independent of the source distribution. We derived the optimal transform which is KLT followed by a diagonal scaling matrix that depends on the bit allocation. This transform is optimal for all sources with fixed rate dithered quantization.
Results : Joint optimization of transform coding and dithered quantization was derived. The optimal transform for dithered quantizers differs from KLT and is optimal for any source distribution (not necessarily Gaussian). Future work will focus on extending the analysis of transform coding to distributed coding with dithered quantizers.
Moreover, we studied the optimal transform coding problem for non-Gaussian sources, with conventional optimal quantizers. We derived the necessary and sufficient condition for optimality of an orthogonal transform and proposed an algorithm, that iteratively imposes this condition for optimality. We extended our approach to multierminal settings, and discovered the optimal transforms for transform coding in networks.
An interesting property of the problem of predictive coding of correlated sources with memory (unlike the case of a singles source) is that reconstruction errors at the decoder are still correlated in time, since time correlation cannot be fully utilized at the encoders by the nature of the problem. Whitened reconstruction errors in audio-visual signals are perceptually preferable, especially at low bitrates. One way of rendering the reconstruction error white is by dithered (randomized) quantization where a pseudo-random dither signal is added to the source prior to entropy coded uniform quantization and identical dither is subtracted at the decoder side. Dithered quantization is known to underperform deterministic quantization at low bitrates due to its use of uniform quantization. As a remedy, we extended the conventional dithered quantization to nonuniform case by employing dithering within the so-called companded domain. We derived the necessary conditions of optimality of such a compander mapping and developed an iterative method to optimize the compander based on the derived conditions. The experimental results show that the nonuniform dithered quantization outperforms the conventional uniform randomized quantizer, while preserving the whiteness of the reconstruction error.
Results : Optimal nonuniform dithered quantization was derived and implemented. Nonuniform dithered quantization significantly outperforms the conventional uniform dithered quantization, and is particularly beneficial for distributed coding of sources with memory, as it avoids correlated reconstruction errors which are perceptually unacceptable. The comparative results are below, where we prposed three new quantization schemes: Quantizer 1 is the unconstrained randomized quantizer, Quantizer 2 is the proposed randomized quantizer with statistical benefits and Quantizer 3 is the deterministic quantizer with identical statistical benefits. As shown, all otuperfom the conventional Uniform Dithered Quantizer significantly.
Variable rate comparison Fixed rate comparison
